
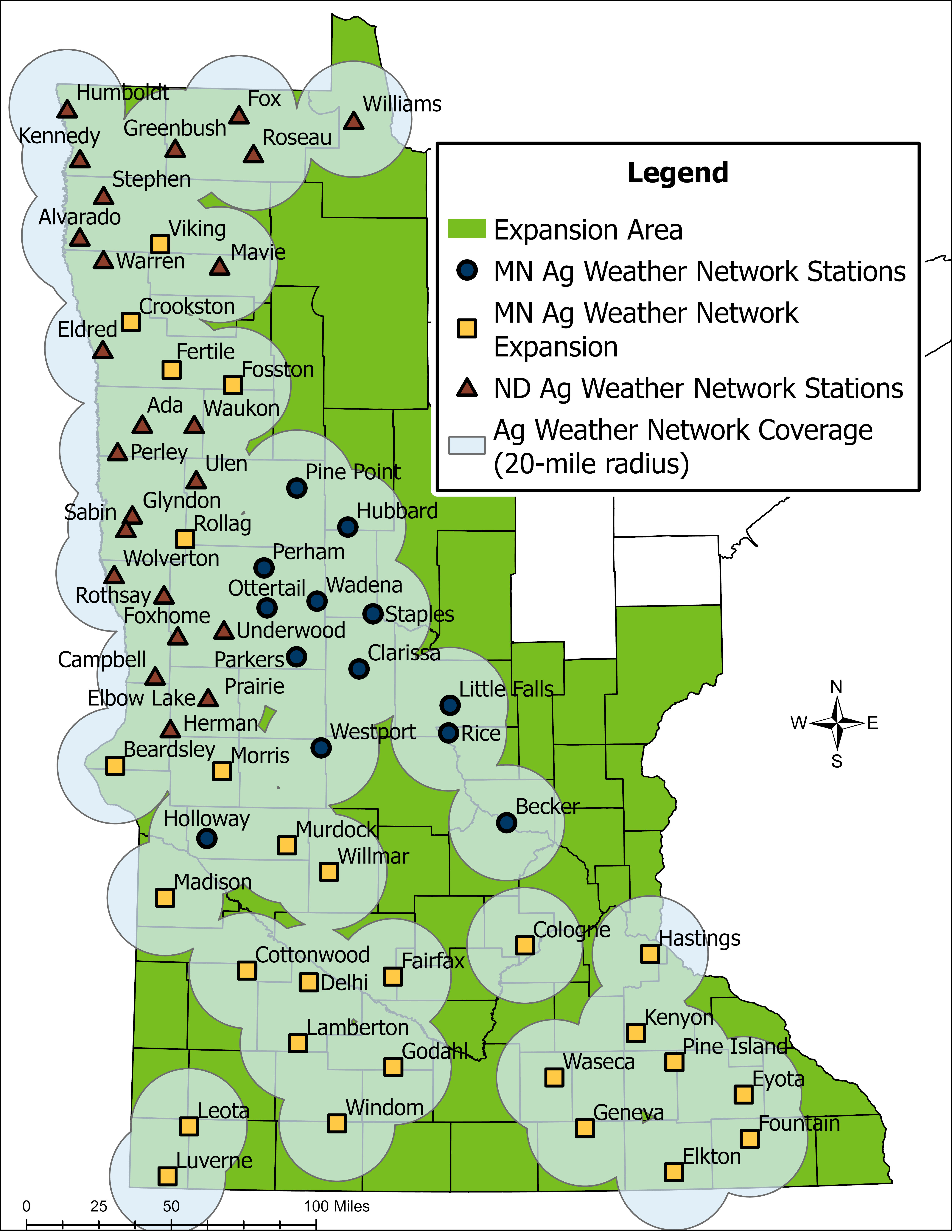
The MDA and local partners operate 40 weather stations in the Minnesota Ag Weather Network (MAWN). Another 24 stations in the state are owned and operated by the North Dakota Ag Weather Network (NDAWN), a vital partner in the project.
Providing accurate and detailed local weather data within 20 miles of ag areas across the state is a goal of the project. Up to 80 total stations may be necessary to achieve this goal.
Information gathered at each site is integrated into NDAWN, which developed tools and applications to make the data readily accessible to the public.
Minnesota station data is available at: ndawn.ndsu.nodak.edu and ndawn.info/centralmn.html.
The network relies upon landowners across the state willing to host weather stations. Each weather station is installed in an area of about 30 feet by 30 feet (0.02 acres) on land not enrolled in the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) or the Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program (CREP) due to program rules. The intent is to operate on each site for at least 50 years. Landowners interested in hosting a station can complete the Minnesota Ag Weather Station Host Application.
Weather Station Details
- Each weather station is solar powered and transmits data over a cellular network every 5 minutes.
- Stations monitor weather up to 33 feet in the air, and soil conditions down to 7.5 feet below the surface, including rain and snow, air temperature and humidity, wind speed, solar radiation, and soil temperature and moisture.
- Research-grade monitoring equipment is used to ensure high-quality and valuable data.
Network Expansion
In 2023, the MDA received funding from the Clean Water Fund to expand the weather station network to agricultural areas statewide (green shading on the map). The initial expansion of about 40 additional weather stations began in 2024 and will be completed in cooperation with local partners over the next few years.
Benefits
Accurate and timely weather information is necessary for many precision agriculture technologies and to help farmers optimize the management of irrigation, manure, fertilizer, and pesticide applications. This improves farm profitability, reduces loss of agricultural inputs, and protects surface water and groundwater. Current and historical weather and soil data also are used for estimating drought progression, flood risk, runoff risk, mapping localized weather conditions and input into various computer modeling efforts used in water resource management and planning.
Data Collected
- Rainfall
- Air temperature
- Wind direction and speed
- Relative humidity
- Dew point temperature
- Soil temperatures to 7.5 feet
- Soil moisture to 40 inches
- Solar radiation
- Snow depth and snow water equivalent
Data and tools available through MAWN with resulting benefits:
Soil temperature:
- Optimize the timing for fall application of fertilizer and manure, and termination of cover crop
- Reduce loss of nutrients, keep nutrients available for next season's crop
- Minimize leaching of nitrate into groundwater
Inversion alert system and wind speed and direction
- Detect temperature inversion and quickly changing weather conditions before pesticide application
- Keep pesticides on target for treatment and reduce the risk of drift
- Prevent off-site movement of pesticides that can drift to nearby surface waters
Irrigation scheduling
- Estimate evapotranspiration to determine crop water needs and optimize irrigation water usage
- Optimize yields and improve water productivity
- Minimize the quantity of water used and the potential leaching of ag chemicals and manure to groundwater
Disease risk forecasting
- Determine periods of disease risk; apply pesticide only when disease risk is high
- Reduce need for preventive pesticide applications
- Reduce unneeded pesticide application and potential water contamination
Runoff risk forecasting
- Forecast potential overland runoff up to 10 days and delay application to prevent runoff
- Reduce runoff loss, keep manure onsite and available to the crop
- Prevent loss of manure or other inputs to surface water
MAWN's expansion is made possible through the support of Minnesota's Clean Water Fund.


